A beginner’s guide to video resolution.
Get the best video quality for your needs by learning how digital video resolution relates to aspect ratio, frame rate and video editing.

Video resolution is the number of pixels contained in each frame.
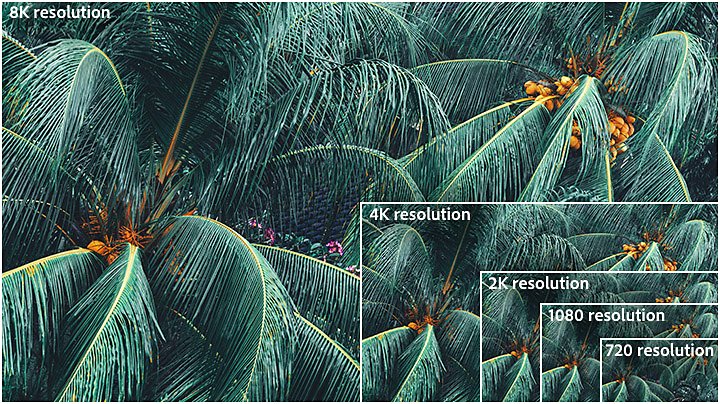
Video resolution determines the amount of detail in your video or how realistic and clear the video appears. It’s measured by the number of pixels contained in the standard aspect ratio of 16:9, the most common aspect ratio for television and computer monitors. A higher number of pixels indicates a higher resolution and a lower number of pixels makes for a low-resolution video. For the common resolutions of 720 and 1080, the naming convention is based on the total number of pixels running in a vertical line down the display area. For 2K, 4K or 8K video, the resolution is named for the number of pixels running in a horizontal line across the frame.

Progressive scan versus interlaced.
The “p” that often appears after a resolution number, as in 1080p, does not stand for pixels. It stands for progressive scan, the typical method for loading the pixels in each new frame of a video. Simply put, this means the pixels in each new frame appear on the screen all at once, which is the optimal scan method for digital media. The alternative method is an interlaced scan, in which the pixels for each new frame load in alternating lines, which saves bandwidth but may cause flickering or blurred lines with fast movement.
Standard definition is no longer the standard.
Previously, resolution has been divided between standard definition (SD video) and high definition (HD video). Anything below 720 is considered standard definition. However, as screen resolutions on computer monitors and televisions continue to improve, it’s less likely for anything to be shot in SD.
The difference between video resolution and frame rate.
Digital videos are made up of thousands of still images played in sequence. While resolution refers to the amount of data in the frame, frame rate refers to how quickly those frames are cycled through, or how many stills are packed into each second. As with video resolution, choose your video’s frame rate based on the type of motion you’re trying to capture and the type of video formats you expect to release to your audience.


Higher resolutions are not always a better choice.
Consider your end deliverable when choosing a resolution. Video resolution affects video size and this presents the same challenges as image resolution. If you were looking to create thumbnails for a website, you wouldn’t want to waste space on your hard drive by saving huge images with high resolutions. If you know your video project is going to be limited to a YouTube video with a maximum display resolution of 1080, don’t waste time and resources by creating your video files in 8K as if they are going to be used in a blockbuster film.
“Of course you always want the best resolution possible,” says director and filmmaker Mike Leonard. “Even though I love the idea of starting as big as possible, what you could end up doing is overwhelming the amount of storage space that the editor is going to need.”
Choosing which HD resolution to shoot in.
Video resolution is like a haircut: You can always decrease a video from a high resolution to a lower one, but there’s no way to magically increase lower resolution footage after it’s been shot. So while you don’t want to waste storage space by going too high, you also want to make sure your resolution is high enough for the various formats where your footage might be seen.

Resolución de 720 (HD)
Se trata de la resolución más baja considerada HDTV; suele hacerse referencia a ella simplemente como “HD”. Aunque la mayoría de los videos se graban al menos en 1080, la resolución de 720 (1280 × 720 pixeles) puede aceptarse para grabar contenido sitio web de pequeño tamaño. No obstante, en la actualidad, la mayoría de las pantallas de computadora son HD, por lo que lo mejor es optar por una resolución superior a la de 720 para el uso en el sitio web y la transmisión.
La resolución de 1080 (1920 × 1080 pixeles), denominada “Full HD”, se convirtió en el estándar del sector para la grabación de videos digitales en HD nítidos que no ocupen todo el espacio de almacenamiento. También es una resolución de pantalla habitual en los dispositivos móviles.
Resolución de 2K o QHD (Quad High Definition)
Los siguientes pasos son la resolución QHD (2560 × 1440 pixeles) o la resolución 2K (2048 × 1080 pixeles). Estos formatos ofrecen más margen de maniobra para la edición de imágenes, las pantallas más grandes y los cambios de marco sin pérdida de calidad.
Esta resolución, denominada 4K y comercializada a menudo como UHD (televisión de ultraalta definición), consta, técnicamente, de 3840 × 2160 pixeles. A la mayoría de los espectadores les parece bastante similar a la 2K, pero ofrece a los cineastas más margen de ampliación y edición. “En realidad, las resoluciones de 2K y 4K sirven para el visionado en salas de cine, o para intensificar los colores o gráficos”, explica la editora y directora de video Margaret Kurniawan. “No existe una diferencia suficientemente notable entre 4K y 2K, a menos que quieras hacer planos más cortos o editar los colores. Por tanto, es importante en la posproducción, pero no afecta mucho al visionado”, agrega.
Resolución de 8K
Los reporteros gráficos no tienen que grabar en 8K (7680 × 4320 pixeles) casi nunca, pero esta opción de altísima resolución es la que deja más espacio para crear efectos sorprendentes o acercar una toma lejana sin que se pixele. “Existen dos razones principales para grabar en 8K. Una son los efectos visuales, ya que contiene más información de pixeles para elementos como los cromas verdes o la rotoscopia. Y la otra es el cambio de marco: se puede cambiar el encuadre a un primer plano sin notar ninguna pérdida de calidad”, explica Leonard.
Grabar con distintas resoluciones
Pueden intentar grabar con diferentes resoluciones HD gratis con la función de cámara de Adobe Premiere Pro. Activa el modo Pro para ajustar la resolución y la velocidad de fotogramas manualmente antes de empezar a grabar. Si tu dispositivo las admite, intenta encontrar las diferentes entre las resoluciones de video de 720, 1080 y 4K.
The next step is picking up a DSLR camera or video camera and playing with the available resolution settings. “The settings on your camera will make or break you,” says Kurniawan. “You need to make# sure that that they're correct and doing what you want before you shoot. And resolution is a big part of that.”
Choose the right resolution for your project ahead of time to save time and space as you edit and create the best footage for your purposes.
Contributors
Haz más con Adobe Premiere Pro.
Puedes crear y edita tus videos estés donde estés y desde un teléfono, una tablet o una computadora. Edita y comparte tus videos de aspecto profesional en las redes sociales.
You might also be interested in…
Mejora videos con el software de edición de videos Adobe Premiere Rush.
Mejora la calidad de los videos con corrección de color y ajustes de audio con estas intuitivas herramientas.
Cómo editar vídeos: todo lo que debes saber.
Aprende los principios de la edición de vídeo y consejos prácticos tanto para pantallas grandes como pequeñas.
Cómo comprimir un video para compartir en redes sociales.
Aprende cómo emplear Adobe Premiere Rush para reducir el tamaño de los archivos y exportar videos.
Experimenting with video effects.
Dive into popular post-production effects and explore the moods and styles each can achieve.
Obtén Adobe Premiere Rush
Puedes crear y comparte videos en línea desde cualquier parte.



